Circlefarming tackles the problems in the food production landscape. How can you take better care of the soil and biodiversity and at the same time produce sufficient quality food in an attractive environment?
Circlefarming believes in the combination and qualities of human labor, existing tools and new technology to make agriculture attractive again.
The Compass on which the work beds, tractor tools and technology are hung is literally the carrier of the concept. With the mix of people, machines and digital technology, Circlefarm knows how to reconnect the farmer with his land and social environment, involve the consumer in agriculture and create space in the crowded Dutch landscape for nature and people. The circular fields are friendly to people, soil and nature and the space between the circles is an oasis for nature, biodiversity and possibly people.
Principles
The Compass
The Compass replaces the tractor and offers the possibility to grow different crops close together: efficient in surface use but also effective in pest and disease control. In addition, a mix of crops provides a mix of insects that can contribute positively to pollination and crop protection and increase biodiversity.
Reshaping the field
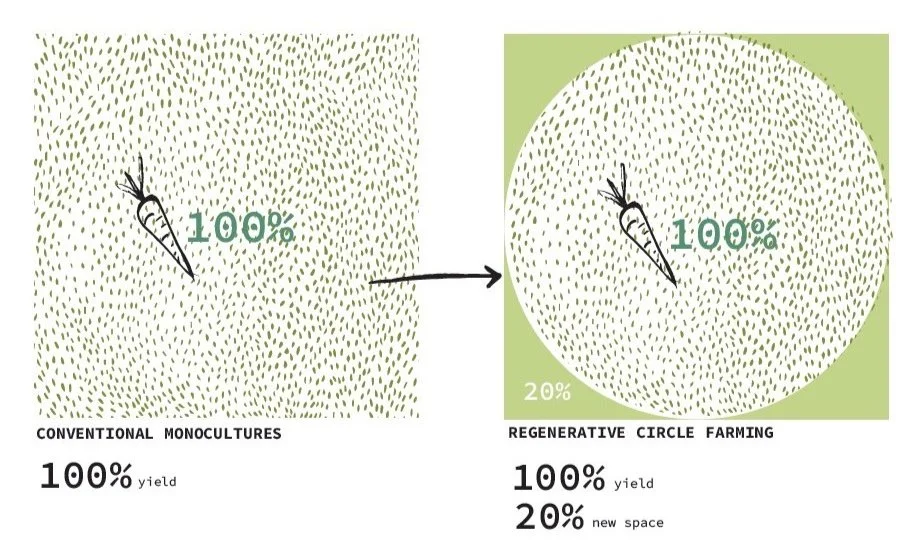
Using the Compass from a central point leads to circular fields. A field with multiple circles thus gets organic spaces in between that can be used for nature, recreation or even living.
Efficient farming
The efficient use of the soil in the circular fields ensures that there is no loss of yield compared to regular agriculture. Circle farming does not require paths for tractors or people because the tools and people float freely over the field, hanging from the Compass.
New technology
New technology such as robotics can also be attached to the arm. Various start-ups are developing these robotics and the technology will reach the market in the coming years. Radars and cameras that are constantly attached to the Compass can collect a lot of data about the field, the crops and, for example, biodiversity.
Sharing knowledge
Field and crop data can be converted into actions for the farmers and participants by a smart platform - set up by Circlefarming - and can contribute to the knowledge for all Circlefarmers. In this way, smaller agricultural initiatives can learn from each other and form a strong force in the agricultural transition.